The global landscape of economic development is often categorized into Less Developed Countries (LDCs) and More Developed Countries (MDCs). This division, while sometimes oversimplified, provides a framework for understanding disparities in various socio-economic indicators and the distinct challenges and opportunities faced by nations across the world. Examining the characteristics, trajectories, and interdependencies of LDCs and MDCs offers valuable insights into the complex dynamics of global development and the ongoing efforts to bridge the development gap.
LDCs vs. MDCs: A Comparative Overview
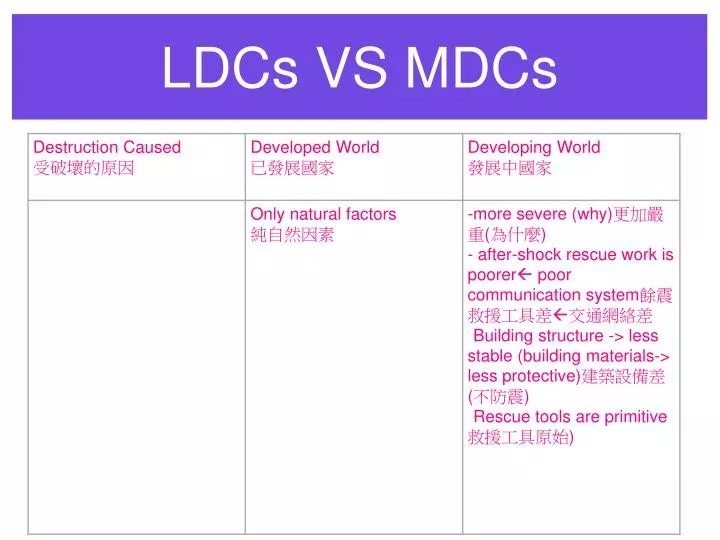
One fundamental distinction between LDCs and MDCs lies in their economic structures. MDCs typically possess diversified economies characterized by robust industrial and service sectors. These sectors contribute significantly to the gross domestic product (GDP) and provide a wide range of employment opportunities. Technological innovation, research and development, and high levels of productivity are hallmarks of MDC economies. In contrast, LDCs often rely heavily on agriculture and primary resource extraction. Their economies may lack diversification, making them vulnerable to fluctuations in commodity prices and external shocks. Manufacturing industries are typically underdeveloped, and the service sector may be limited in scope and sophistication. This economic structure often results in lower overall productivity and limited opportunities for upward mobility.
Another key difference is the level of human development. MDCs generally exhibit higher levels of human development, as measured by indicators such as life expectancy, education attainment, and access to healthcare. These countries have invested heavily in education and healthcare systems, resulting in a more skilled and healthy workforce. Consequently, MDCs often have lower rates of infant mortality, higher literacy rates, and longer life expectancies. LDCs, on the other hand, often face significant challenges in human development. Limited access to quality education, inadequate healthcare infrastructure, and poor sanitation can contribute to lower life expectancies, higher rates of disease, and lower levels of educational attainment. Addressing these human development challenges is crucial for LDCs to unlock their economic potential and improve the overall well-being of their populations.
Furthermore, LDCs and MDCs differ significantly in their levels of technological advancement. MDCs are at the forefront of technological innovation, driving advancements in areas such as information technology, biotechnology, and renewable energy. These countries invest heavily in research and development, fostering a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship. The widespread adoption of technology in MDCs has led to increased productivity, improved communication, and greater access to information. LDCs, however, often lag behind in technological adoption. Limited access to technology, coupled with a lack of skilled personnel and inadequate infrastructure, can hinder their ability to compete in the global economy. Bridging the technology gap is essential for LDCs to accelerate their economic development and improve their competitiveness.
The political and institutional frameworks also play a crucial role in differentiating LDCs and MDCs. MDCs generally have stable political systems, strong institutions, and well-established rule of law. These factors create a conducive environment for investment, innovation, and economic growth. Transparent governance, protection of property rights, and efficient regulatory frameworks are hallmarks of MDC political and institutional systems. LDCs, however, may face challenges related to political instability, corruption, weak institutions, and lack of rule of law. These factors can deter investment, hinder economic development, and undermine social progress. Strengthening governance, promoting transparency, and establishing effective institutions are essential for LDCs to create a stable and predictable environment for sustainable development.
Trade patterns also reflect the differences between LDCs and MDCs. MDCs tend to engage in diversified trade, exporting a wide range of manufactured goods and services. They often have strong trading relationships with other MDCs, forming complex global value chains. LDCs, on the other hand, often rely on the export of primary commodities, such as agricultural products and raw materials. This dependence on commodity exports makes them vulnerable to price fluctuations and terms of trade shocks. Diversifying their export base and developing value-added industries is crucial for LDCs to improve their trade performance and reduce their vulnerability to external shocks.
Industrialization: A Pathway for Development

Industrialization has historically been a key driver of economic development. MDCs underwent significant industrial transformations in the 19th and 20th centuries, which led to increased productivity, higher incomes, and improved living standards. The process of industrialization involves a shift from agriculture and primary resource extraction towards manufacturing and industry. This transition is typically accompanied by technological innovation, increased investment in infrastructure, and the development of a skilled workforce. The industrialization of MDCs created new employment opportunities, stimulated economic growth, and transformed their societies.
For LDCs, industrialization presents a significant opportunity to accelerate their economic development and improve the living standards of their populations. By developing their manufacturing industries, LDCs can diversify their economies, reduce their dependence on commodity exports, and create new employment opportunities. However, the process of industrialization in LDCs faces several challenges. These challenges include a lack of capital, inadequate infrastructure, a shortage of skilled labor, and competition from established industries in MDCs. Overcoming these challenges requires a concerted effort from governments, businesses, and international organizations.
Several strategies can be employed to promote industrialization in LDCs. These strategies include attracting foreign direct investment (FDI), investing in education and training, developing infrastructure, and promoting innovation. FDI can provide LDCs with access to capital, technology, and managerial expertise. Investing in education and training can help to develop a skilled workforce capable of supporting industrial development. Developing infrastructure, such as roads, ports, and power plants, can improve the competitiveness of LDC industries. Promoting innovation can help LDCs to develop new products and services that can compete in global markets.
In addition to these domestic strategies, international cooperation can play a crucial role in supporting industrialization in LDCs. MDCs can provide LDCs with technical assistance, financial support, and preferential access to their markets. International organizations, such as the World Bank and the United Nations, can provide LDCs with policy advice and financial assistance. By working together, LDCs and MDCs can create a more equitable and prosperous global economy.
The path to development is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Each nation must tailor its strategies to its unique circumstances and leverage its specific strengths. However, understanding the fundamental differences between LDCs and MDCs, recognizing the transformative potential of industrialization, and fostering international collaboration are essential steps towards building a more equitable and sustainable world for all.
If you are looking for Industrialization of MDCs and LDCs by Zachary Howard on Prezi you’ve came to the right place. We have 5 Pics about Industrialization of MDCs and LDCs by Zachary Howard on Prezi like MDCS and LDCS | PDF, Ldçs | PDF and also MDC's vs. LDC's by Keily Meador on Prezi. Here you go:
Industrialization Of MDCs And LDCs By Zachary Howard On Prezi

prezi.com
prezi
MDCS And LDCS | PDF

www.scribd.com
Ldçs | PDF

www.scribd.com
MDC's Vs. LDC's By Keily Meador On Prezi

prezi.com
ldc mdc vs mdcs
PPT – LDCs VS MDCs PowerPoint Presentation, Free Download – ID:4256405

www.slideserve.com
Mdc's vs. ldc's by keily meador on prezi. Ldçs. Ldc mdc vs mdcs