Alright, lemme break this down for y’all. We got some info ’bout parliamentary systems and parliaments in general. We gonna take this info and turn it into somethin’ y’all can understand. We ain’t gonna get all caught up in the jargon, just keepin’ it real.
Look, understanding how governments work can feel like trying to decipher a whole ‘nother language. All them big words and fancy terms? They can make your head spin. But don’t sweat it. We gonna break down this parliamentary system thing step by step, keepin’ it simple and straight to the point. We gonna talk ’bout how it works, what makes it different from other kinds of governments, and why it matters to everyday folks like you and me. So, grab your coffee, sit back, and let’s get into it.
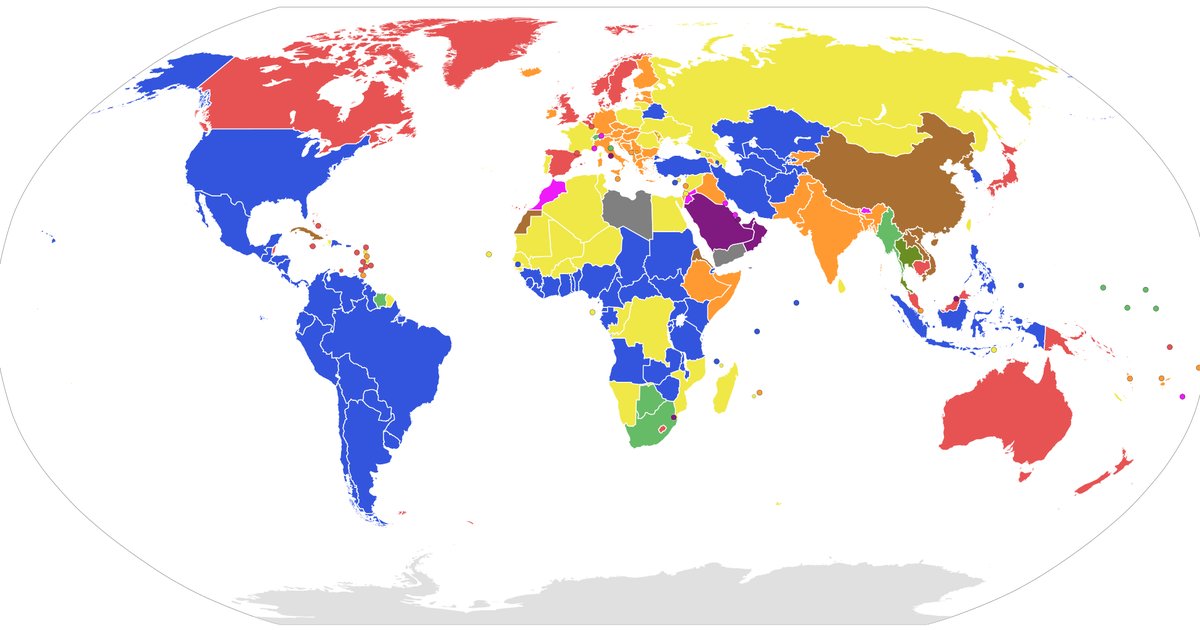
Parliamentary Systems: It Ain’t One Size Fits All
Now, when we talkin’ ’bout parliamentary systems, you gotta understand one thing: they ain’t all the same. Think of it like this: you got different flavors of ice cream. They all ice cream, but chocolate ain’t vanilla, and strawberry ain’t got nothin’ to do with cookies and cream. Same deal with parliamentary systems. They got the same basic idea – a parliament makin’ the laws and holdin’ the government accountable – but the details? That’s where things get interesting. You might have different ways of electin’ folks, different powers for the prime minister or president, and different roles for the upper and lower houses of parliament. Some might have a ceremonial head of state like a queen or king, while others might have an elected president. The devil’s in the details, ya hear?
For instance, some parliaments are bicameral, meaning they have two chambers or houses – like the U.S. Congress with the Senate and the House of Representatives. Other parliamentary systems are unicameral, meaning they only got one legislative chamber. The powers and responsibilities of each chamber can also differ significantly. In some systems, the upper chamber has more influence, while in others, it’s largely ceremonial. All these variations can affect how laws are made and how the government operates. So, don’t just assume every parliamentary system works exactly the same, ’cause they don’t. Keep an open mind, and pay attention to the specifics.
Another key variation lies in the relationship between the executive and legislative branches. In some parliamentary systems, the prime minister, who leads the government, is directly accountable to the parliament and can be removed from office through a vote of no confidence. This means that if the parliament loses faith in the prime minister, they can boot ’em out. In other systems, the prime minister might have more independence. This can affect the stability of the government and the ability of the parliament to hold the executive branch accountable. Understanding these nuances is key to understandin’ how power is distributed and exercised within each system.
Furthermore, the electoral system used to elect members of parliament can also significantly shape the political landscape. Different electoral systems, such as proportional representation or first-past-the-post, can lead to different outcomes in terms of party representation and government formation. Proportional representation, for example, tends to result in more coalition governments, where multiple parties must work together to form a majority. First-past-the-post systems, on the other hand, often lead to single-party governments. These differences can affect the stability and effectiveness of the government, as well as the representation of different groups and interests in society.
Countries and Their Parliaments: A Global Perspective
Now, let’s zoom out and look at some real-world examples. Different countries, different parliaments, different ways of doin’ things. Look at the United Kingdom, the OG parliamentary system. They got the House of Commons and the House of Lords, along with a monarch who’s mostly a figurehead these days. Then you got Canada, another parliamentary democracy, but with a slightly different setup. India, the world’s largest democracy, has a parliamentary system, but it’s adapted to the country’s unique culture and history. Each country’s parliament reflects its own specific circumstances and challenges.
Think about the separation of powers. In some parliamentary systems, the lines between the executive and legislative branches are blurred, while in others, they’re more distinct. The role of the judiciary also varies. In some countries, the courts have the power to review laws passed by parliament and strike them down if they’re unconstitutional. In others, the courts have a more limited role. These differences in the separation of powers can have a significant impact on the balance of power within the government and the protection of individual rights and freedoms. Understanding these differences is essential for understanding how each country’s parliamentary system operates in practice.
Take Germany, for example. Their parliament, the Bundestag, plays a central role in shaping policy and holding the government accountable. But the German system also emphasizes the importance of federalism, with significant power devolved to the states. This means that the states have a say in many areas of policy, and the federal government must work with them to implement its agenda. This federal structure adds another layer of complexity to the German parliamentary system.
Then you got countries like Italy, which have experienced frequent changes in government. This can be due to a variety of factors, including political instability, complex electoral systems, and the presence of multiple parties. The frequent changes in government can make it difficult to implement long-term policies and can undermine public confidence in the political system. Other countries, like New Zealand, have experimented with electoral reforms to try to improve representation and stability. New Zealand switched from a first-past-the-post system to a mixed-member proportional system in the 1990s, which has led to more diverse representation in parliament.
And don’t forget about the role of civil society. In a healthy parliamentary democracy, civil society organizations, such as advocacy groups, non-profits, and think tanks, play an important role in holding the government accountable and advocating for the interests of their members. These organizations can provide valuable information and analysis to parliamentarians, organize public campaigns, and monitor government policies. A vibrant civil society is essential for ensuring that the government is responsive to the needs and concerns of the people.
So, the next time you hear about a country’s parliament, don’t just assume you know how it works. Take the time to learn about the specifics of that particular system. Understanding the nuances of different parliamentary systems is essential for understandin’ global politics and for engaging in informed discussions about democracy and governance. It ain’t always easy, but it’s definitely worth the effort. Remember, knowledge is power, and the more you understand about how the world works, the more you can influence it.
Ultimately, the effectiveness of a parliamentary system depends on a variety of factors, including the quality of its political institutions, the strength of its civil society, and the level of public participation. A well-functioning parliamentary system can provide a stable and responsive government that is accountable to the people. But a poorly functioning system can lead to political instability, corruption, and a lack of public trust. That’s why it’s so important to understand the different ways in which parliamentary systems can be designed and operated, and to work to strengthen these systems around the world.
In conclusion, parliamentary systems of government are complex and varied. While they share some common features, such as a parliament that makes laws and holds the government accountable, the specific details of each system can differ significantly. Understanding these differences is essential for understandin’ global politics and for engaging in informed discussions about democracy and governance. So, keep learnin’, keep askin’ questions, and keep fightin’ for a better world. Peace out.
If you are searching about Parliamentary Democratic Countries you’ve visit to the right web. We have 5 Images about Parliamentary Democratic Countries like Parliamentary Systems of Government Can Vary in Specific Details From, Parliamentary system Countries List | Countries Ruled by Parliamentary and also Parliamentary Systems of Government Can Vary in Specific Details From. Here you go:
Parliamentary Democratic Countries
www.governmentvs.com
republic parliamentary democracy countries democratic
Parliamentary System Countries Quiz – By Yousif_alkandri
www.sporcle.com
parliamentary countries system
Parliamentary System Countries List | Countries Ruled By Parliamentary
www.ranker.com
countries parliamentary system ruled list
Parliamentary Systems Of Government Can Vary In Specific Details From
www.scribd.com
Countries And Its Parliament | PDF | Separation Of Powers | Government
www.scribd.com
Parliamentary countries system. Countries parliamentary system ruled list. Parliamentary system countries quiz