Exploring the diverse tapestry of nations across the globe, one can appreciate the richness and variety that each country brings to the world stage. This exploration often begins with a simple exercise: categorizing countries based on alphabetical order. Today, we delve into the fascinating list of countries that proudly begin with the letter “D,” uncovering some of their unique characteristics, historical significance, and cultural contributions. The following overview provides a glimpse into the distinct identities of these nations, showcasing their geographical diversity, economic landscapes, and political structures.
Dominica
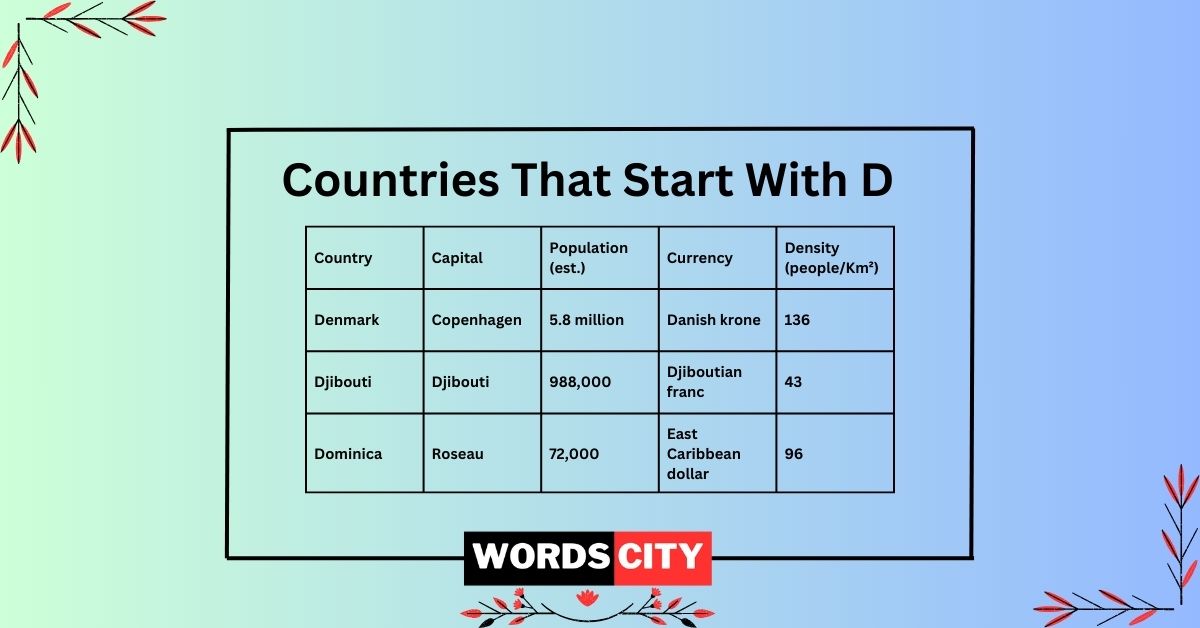
Dominica, officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is a captivating island nation nestled in the Lesser Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea. Often referred to as the “Nature Island” of the Caribbean, Dominica boasts a remarkably diverse landscape, characterized by verdant rainforests, cascading waterfalls, and towering volcanic peaks. Unlike many of its Caribbean counterparts, Dominica has largely eschewed mass tourism, opting instead to preserve its pristine natural environment and promote eco-tourism. This commitment to sustainability has allowed Dominica to maintain its unique biodiversity, making it a haven for nature enthusiasts and adventure seekers.
The island’s economy is primarily driven by agriculture, with bananas serving as a major export crop. However, in recent years, the government has actively sought to diversify the economy through investments in tourism, offshore financial services, and renewable energy. Dominica’s political system is based on a parliamentary democracy, with a president as head of state and a prime minister as head of government. The island’s history is marked by European colonization, primarily by the French and British, before it gained independence in 1978. The cultural heritage of Dominica reflects its diverse history, with influences from African, European, and indigenous traditions. This blend of cultures is evident in the island’s cuisine, music, and artistic expressions.
Dominica’s commitment to environmental protection is particularly noteworthy. The island has established several national parks and reserves to safeguard its unique ecosystems. These protected areas are home to a wide array of plant and animal species, including the iconic Sisserou Parrot, Dominica’s national bird. The island’s rugged terrain and dense rainforests offer unparalleled opportunities for hiking, birdwatching, and canyoning. The Morne Trois Pitons National Park, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is a prime example of Dominica’s natural beauty.
Dominica faces challenges related to its vulnerability to natural disasters, such as hurricanes and tropical storms. The island has experienced several devastating hurricanes in recent years, highlighting the importance of climate resilience and disaster preparedness. Despite these challenges, Dominica remains a resilient and vibrant nation, committed to sustainable development and the preservation of its natural heritage. The island’s unique blend of natural beauty, cultural richness, and commitment to sustainability makes it a truly special destination.
Denmark
Denmark, officially the Kingdom of Denmark, is a Scandinavian nation renowned for its high quality of life, progressive social policies, and rich cultural heritage. Situated in Northern Europe, Denmark consists of the Jutland Peninsula and numerous islands, making it a maritime nation with a strong connection to the sea. Copenhagen, the capital city, is a vibrant metropolis known for its iconic landmarks, innovative design, and commitment to sustainability. Denmark’s history is deeply intertwined with the history of Scandinavia, marked by Viking Age explorations, medieval kingdoms, and a long tradition of maritime trade.
Denmark boasts a highly developed economy, characterized by a strong welfare state, a skilled workforce, and a focus on innovation. The country is a leader in renewable energy, particularly wind power, and has set ambitious goals for reducing its carbon footprint. Denmark’s agricultural sector is also highly productive, with a focus on sustainable farming practices. The country’s political system is based on a constitutional monarchy, with a queen as head of state and a prime minister as head of government. Denmark is a member of the European Union, but it retains its own currency, the Danish krone.
Denmark’s cultural heritage is rich and diverse, with influences from Viking traditions, medieval art, and modern design. The country is home to numerous museums, art galleries, and historical sites that showcase its cultural heritage. Danish design is particularly renowned, with its emphasis on functionality, simplicity, and aesthetics. The concept of “hygge,” a Danish word that describes a feeling of coziness, contentment, and well-being, is deeply ingrained in Danish culture.
Denmark’s commitment to social welfare is a defining characteristic of its society. The country provides its citizens with universal healthcare, free education, and generous social security benefits. This commitment to social equality has contributed to Denmark’s high quality of life and its reputation as one of the happiest countries in the world. Denmark’s education system is highly regarded, with a focus on critical thinking, creativity, and innovation. The country’s universities are internationally recognized for their research and academic excellence.
Denmark plays an active role in international affairs, promoting peace, security, and sustainable development. The country is a strong supporter of international cooperation and is committed to addressing global challenges such as climate change, poverty, and inequality. Denmark’s foreign policy is guided by its commitment to human rights, democracy, and the rule of law.
Denmark’s commitment to innovation is evident in its thriving tech sector and its focus on research and development. The country is a leader in fields such as biotechnology, clean technology, and digital technology. Denmark’s strong entrepreneurial ecosystem supports the growth of new businesses and fosters innovation across various sectors. The country’s vibrant cultural scene, its commitment to social welfare, and its focus on innovation make it a dynamic and forward-thinking nation. Denmark’s blend of tradition and modernity creates a unique and appealing atmosphere for both residents and visitors. The country’s commitment to sustainability and its focus on quality of life make it a model for other nations to emulate.
Djibouti
Djibouti, officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a strategically located nation in the Horn of Africa, bordering Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Somalia. Its location at the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait, a crucial waterway connecting the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden, has made it a significant hub for maritime trade and military operations. Djibouti’s landscape is predominantly arid and semi-arid, characterized by volcanic formations, salt lakes, and desert plains. The country’s climate is hot and dry, with limited rainfall throughout the year.
Djibouti’s economy is largely dependent on its strategic location and its role as a transportation and logistics hub. The Port of Djibouti is a major gateway for trade between Africa, Asia, and Europe. The country also hosts several foreign military bases, including those of the United States, France, and China. These bases contribute significantly to Djibouti’s economy through rental fees and related services. Djibouti’s political system is based on a presidential republic, with a president as head of state and a prime minister as head of government. The country’s history is marked by French colonization, before it gained independence in 1977.
Djibouti’s cultural heritage reflects its diverse history and its location at the crossroads of Africa and the Middle East. The country’s population is predominantly Muslim, with a mix of Somali and Afar ethnic groups. Arabic and French are the official languages, while Somali and Afar are also widely spoken. Djibouti’s cuisine is influenced by Arab, Somali, and French culinary traditions. The country’s music and dance reflect its diverse cultural heritage.
Djibouti faces challenges related to its limited natural resources, its arid climate, and its dependence on foreign aid. The country also grapples with high unemployment rates and poverty. However, Djibouti has made progress in recent years in diversifying its economy, improving its infrastructure, and promoting education and healthcare. The government has implemented policies to attract foreign investment, develop its tourism sector, and improve its business environment.
Djibouti’s strategic location continues to be a key asset for the country. The government is working to leverage this advantage by expanding its port facilities, developing its logistics infrastructure, and promoting its role as a regional hub for trade and transportation. Djibouti is also seeking to become a leader in renewable energy, with plans to develop solar and wind power projects.
Djibouti’s commitment to regional stability is reflected in its efforts to promote peace and security in the Horn of Africa. The country has played a role in mediating conflicts and promoting dialogue between neighboring countries. Djibouti’s foreign policy is guided by its commitment to multilateralism and its desire to foster closer ties with its regional and international partners. The country’s efforts to diversify its economy, improve its infrastructure, and promote regional stability are essential for its long-term development and prosperity.
Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic, officially the República Dominicana, is a vibrant nation occupying the eastern two-thirds of the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean archipelago. Sharing its western border with Haiti, the Dominican Republic boasts a rich history, diverse culture, and stunning natural beauty. From pristine beaches and turquoise waters to towering mountains and lush valleys, the Dominican Republic offers a captivating blend of landscapes and experiences.
Tourism is a major driver of the Dominican Republic’s economy, attracting millions of visitors each year to its numerous resorts, historical sites, and natural attractions. The country is renowned for its all-inclusive resorts, which offer a convenient and luxurious vacation experience. However, the Dominican Republic also offers a wealth of opportunities for independent travelers to explore its diverse regions, discover its cultural heritage, and immerse themselves in its vibrant atmosphere.
The Dominican Republic’s history is deeply intertwined with the history of the Caribbean. It was one of the first European settlements in the Americas, founded by Christopher Columbus in 1496. The country’s colonial past is evident in its architecture, its language, and its cultural traditions. Santo Domingo, the capital city, is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, showcasing a wealth of colonial-era buildings and historical landmarks.
The Dominican Republic’s culture is a blend of Spanish, African, and indigenous influences. This cultural fusion is evident in its music, its dance, its cuisine, and its artistic expressions. Merengue and bachata are two popular musical genres that originated in the Dominican Republic and have gained international recognition. The country’s cuisine is a flavorful mix of Spanish, African, and Caribbean dishes, featuring ingredients such as rice, beans, plantains, and seafood.
The Dominican Republic’s political system is based on a presidential republic, with a president as head of state and head of government. The country has a long history of political instability, but it has made progress in recent years in strengthening its democratic institutions and promoting good governance. The Dominican Republic faces challenges related to poverty, inequality, and corruption, but it is committed to addressing these issues and improving the lives of its citizens.
The Dominican Republic’s commitment to sustainable development is reflected in its efforts to protect its natural resources, promote renewable energy, and improve its environmental management practices. The country is home to numerous national parks and reserves that protect its biodiversity and its natural beauty. The Dominican Republic is also working to develop its eco-tourism sector, offering visitors opportunities to experience its natural wonders in a sustainable and responsible way.
The Dominican Republic’s vibrant culture, its stunning natural beauty, and its commitment to sustainable development make it a unique and appealing destination for travelers from around the world. The country’s welcoming atmosphere, its friendly people, and its rich history create an unforgettable experience for visitors. The Dominican Republic’s blend of tradition and modernity, its vibrant culture, and its stunning natural beauty make it a captivating nation that continues to inspire and enchant.
If you are searching about Countries That Start With the Letter D – WorldAtlas you’ve came to the right page. We have 5 Images about Countries That Start With the Letter D – WorldAtlas like Countries That Start With the Letter D – WorldAtlas, Countries That Start With The Letter D – WorldAtlas and also Countries That Start With The Letter D – WorldAtlas. Here it is:
Countries That Start With The Letter D – WorldAtlas
www.worldatlas.com
worldatlas world
Countries That Start With The Letter D – WorldAtlas
www.worldatlas.com
Countries That Start With D: 05 Popular Countries Beginning With D • 7ESL
7esl.com
Countries That Start With D In The World
tourinplanet.com
Countries That Start With D : Capitals, Currency And Population – Words
wordscity.com
Countries that start with the letter d. Countries that start with d in the world. Countries that start with the letter d