Alright, let’s dive into the fascinating world of global development and take a closer look at the differences between More Developed Countries (MDCs) and Less Developed Countries (LDCs). It’s a complex topic, full of nuances and interconnected factors, but understanding these distinctions is crucial for grasping the global landscape we live in. We’ll explore key indicators like economic prosperity, health, education, and technology, painting a picture of the realities on the ground.
Comparing Development Levels
Let’s start with the basics. MDCs, often referred to as developed or industrialized nations, typically boast advanced economies with a large service sector and a significant presence in high-tech industries. Think countries like the United States, Japan, Germany, and the United Kingdom. Their economies are generally characterized by high levels of productivity, technological innovation, and capital accumulation. They have well-established infrastructure, including reliable transportation networks, robust communication systems, and advanced healthcare facilities. These factors contribute to a higher standard of living for their citizens.
LDCs, on the other hand, are often characterized by economies heavily reliant on agriculture and extraction of raw materials. Industrialization is often limited, and manufacturing industries are frequently underdeveloped. Examples of LDCs include countries in Sub-Saharan Africa, parts of Asia, and some nations in Latin America. These countries often face challenges such as limited access to capital, inadequate infrastructure, and a lack of skilled labor. These factors can hinder economic growth and development, contributing to lower standards of living for their populations.
One of the most striking differences lies in economic indicators. MDCs typically have significantly higher Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita, reflecting greater economic output and income per person. This higher GDP translates into increased consumer spending, investment, and overall economic activity. They also tend to have more diversified economies, with a wider range of industries contributing to their overall wealth. In contrast, LDCs often struggle with low GDP per capita, indicating limited economic opportunities and widespread poverty. Their economies may be heavily dependent on a few key industries, making them vulnerable to fluctuations in global commodity prices.
Health and Well-being
The disparities between MDCs and LDCs are not just limited to economic factors; they extend to health and well-being. MDCs generally have significantly higher life expectancies and lower infant mortality rates, reflecting access to better healthcare, sanitation, and nutrition. Advanced medical technologies, well-trained healthcare professionals, and robust public health systems contribute to improved health outcomes. LDCs, conversely, often face significant challenges in healthcare delivery. Limited access to clean water, sanitation, and nutritious food contributes to higher rates of infectious diseases and malnutrition. Healthcare systems may be underfunded and understaffed, making it difficult to provide adequate medical care to the population.
Education is another key indicator that highlights the differences between MDCs and LDCs. MDCs typically have high literacy rates and widespread access to quality education at all levels, from primary school to higher education. Investing in education is considered a priority, as it equips individuals with the skills and knowledge necessary to participate in the modern economy. LDCs, however, often struggle with low literacy rates and limited access to education, particularly for girls and women. Schools may be under-resourced, and teachers may be poorly trained. These challenges can limit opportunities for individuals to improve their lives and contribute to economic development.
Technology and Infrastructure
Technology and infrastructure are also vital components that separate MDCs and LDCs. MDCs have advanced technological infrastructure, including high-speed internet, widespread access to computers and mobile devices, and well-developed communication networks. This technological infrastructure facilitates innovation, productivity, and economic growth. LDCs, on the other hand, often lack access to basic technology and infrastructure. Limited internet connectivity, unreliable electricity supply, and poor transportation networks can hinder economic development and limit opportunities for individuals and businesses.
MDC vs. LDC

It’s important to recognize that the distinction between MDCs and LDCs is not always clear-cut. There is a spectrum of development levels, and some countries may exhibit characteristics of both. Furthermore, the term “developing country” is often used to describe nations that are in the process of transitioning from LDC status to MDC status. This process typically involves sustained economic growth, improvements in health and education, and investments in infrastructure.
Globalization has also played a significant role in shaping the development landscape. Increased trade, investment, and technological transfers have the potential to accelerate economic growth in LDCs and promote convergence with MDCs. However, globalization can also create challenges, such as increased competition, exploitation of labor, and environmental degradation. It is crucial for policymakers to implement policies that maximize the benefits of globalization while mitigating its potential risks.
Addressing the disparities between MDCs and LDCs requires a multifaceted approach. Investing in education, healthcare, and infrastructure is essential for promoting sustainable development. Promoting good governance, reducing corruption, and fostering a stable political environment are also critical. Furthermore, international cooperation is vital for providing financial assistance, technical expertise, and debt relief to LDCs. By working together, the global community can help to create a more equitable and prosperous world for all.
Finally, it’s vital to remember that development is not solely about economic growth. It also encompasses social, cultural, and environmental dimensions. Sustainable development aims to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. This requires a holistic approach that considers the interconnectedness of economic, social, and environmental issues. By pursuing sustainable development, we can create a world that is not only prosperous but also just and equitable.
Understanding the differences between MDCs and LDCs is crucial for navigating the complex challenges of the 21st century. By acknowledging the disparities that exist and working together to address them, we can strive towards a more equitable and sustainable future for all.
If you are looking for LDC /MDC #3 by Emmanuel a-emmanuel@ on Prezi you’ve came to the right page. We have 5 Images about LDC /MDC #3 by Emmanuel a-emmanuel@ on Prezi like MDC vs LDC by Nick Trammell on Prezi, MDC vs. LDC by Ja'Tori Myers on Prezi and also MDC vs. LDC by Ja'Tori Myers on Prezi. Read more:
LDC /MDC #3 By Emmanuel A-emmanuel@ On Prezi

prezi.com
LDC Vs MDC Country Comparison By Angelica Vasquez On Prezi

prezi.com
MDC Vs. LDC By Ja'Tori Myers On Prezi

prezi.com
vs prezi
MDC VS LDC PP By Cesar Miranda On Prezi
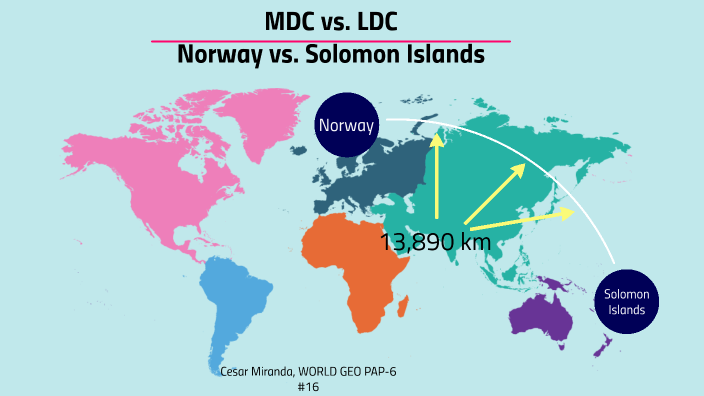
prezi.com
MDC Vs LDC By Nick Trammell On Prezi
prezi.com
ldc mdc vs
Mdc vs ldc pp by cesar miranda on prezi. Mdc vs. ldc by ja'tori myers on prezi. Vs prezi