Ah, Antarctica! Such a mysterious and intriguing place. Many think it’s just a big block of ice, but it’s so much more than that. It’s a continent of stark beauty, scientific discovery, and international cooperation. People from all over the world are drawn to its icy shores, each with their own research, explorations, and dreams. Let’s delve into this fascinating land and explore the nations with a presence there.
The Allure of the South: Nations Laying Claim
While no single nation owns Antarctica outright, several countries have laid claim to portions of the continent. These claims, however, are largely frozen under the Antarctic Treaty System, an international agreement promoting peace and scientific collaboration. This treaty ensures that Antarctica remains a place for peaceful purposes and scientific research, rather than a territory for national exploitation. But who are these nations asserting their historical or geographic connections to the icy south? Let’s take a look:
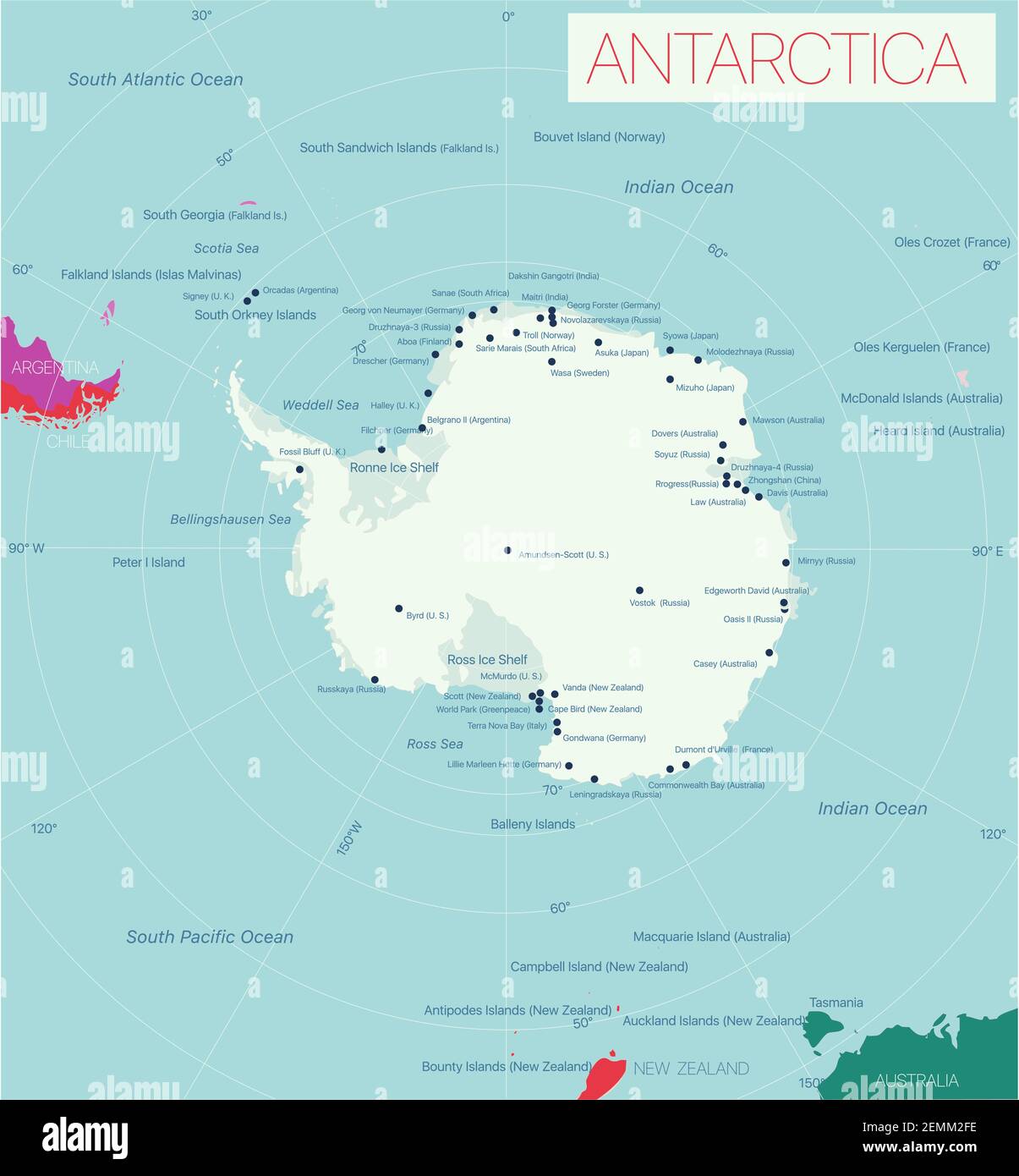
Argentina: With a sector overlapping the British and Chilean claims, Argentina considers a large portion of the Antarctic Peninsula and surrounding areas to be part of its national territory. They maintain a continuous presence through research stations, emphasizing their historical activities in the region. Their claim is based on proximity and long-standing research efforts.
Australia: Laying claim to the largest sector, Australia asserts sovereignty over a vast expanse of East Antarctica. Their claim dates back to early exploration and scientific expeditions. Australia has a strong commitment to Antarctic research and environmental protection.
Chile: Like Argentina, Chile’s claim overlaps with that of Britain. They view their sector as a natural extension of their territory, citing geographic proximity and historical connections. They have a significant presence in the Antarctic Peninsula.
France: France claims Adélie Land, a relatively small but significant sector along the coast of East Antarctica. This claim is based on early French explorations and scientific research. France maintains a research station in this region.
New Zealand: Laying claim to the Ross Dependency, New Zealand’s sector includes the Ross Ice Shelf and a portion of East Antarctica. Their claim is rooted in their historical exploration and administration of the region. The Ross Ice Shelf is a particularly important area for scientific research.
Norway: Norway claims Queen Maud Land, a large sector in East Antarctica. Their claim is based on early Norwegian expeditions and exploration. Norway has a long history of whaling and exploration in the Antarctic region.
United Kingdom: The UK’s claim encompasses a significant portion of the Antarctic Peninsula and surrounding areas. Their claim is based on early British explorations and scientific research. The British Antarctic Survey conducts extensive research in the region.
Beyond Claims: Active Participants in Antarctic Research

While only a handful of nations have territorial claims, many more participate in Antarctic research and activities. These countries maintain research stations, conduct scientific studies, and contribute to the international understanding of this unique continent. Their presence is vital for advancing our knowledge of climate change, biodiversity, and the Earth’s history. Let’s highlight some of the key players:
United States: With a significant presence at McMurdo Station, the largest research facility in Antarctica, the United States plays a crucial role in scientific research. Their research spans a wide range of disciplines, including glaciology, biology, and atmospheric science. McMurdo Station serves as a logistical hub for many Antarctic expeditions.
Russia: Russia maintains several research stations in Antarctica, continuing the legacy of Soviet exploration and research. Their research focuses on a variety of fields, including geology, geophysics, and climate studies. Vostok Station, located deep within the continent, is renowned for its discovery of Lake Vostok, a subglacial lake.
China: With a growing presence in Antarctica, China operates several research stations and conducts extensive scientific studies. Their research focuses on a wide range of topics, including climate change, glaciology, and marine biology. China’s increasing involvement reflects its growing scientific capabilities and interest in the Antarctic environment.
Germany: Germany operates the Neumayer Station III, a state-of-the-art research facility located on the Ekström Ice Shelf. Their research focuses on atmospheric science, geophysics, and marine biology. The station is designed to operate year-round, providing valuable data throughout the Antarctic seasons.
Italy: Italy maintains the Mario Zucchelli Station in Terra Nova Bay. This station is primarily used during the Antarctic summer and supports research in various fields, including glaciology, geology, and marine biology.
South Korea: South Korea operates the Jang Bogo Station in Terra Nova Bay and the King Sejong Station on King George Island. Their research focuses on various aspects of Antarctic science, including climate change, glaciology, and marine ecology.
India: India has two active research stations in Antarctica, Maitri and Bharati. These stations support research in a variety of fields, including glaciology, geology, and atmospheric science. India’s involvement in Antarctic research reflects its commitment to scientific exploration and international cooperation.
Japan: Japan operates the Syowa Station, one of the oldest research stations in Antarctica. Their research focuses on a wide range of topics, including atmospheric science, glaciology, and biology. Japan has a long history of involvement in Antarctic research.
The Future of Antarctica: Collaboration and Conservation
The Antarctic Treaty System has been instrumental in maintaining peace and promoting scientific collaboration in Antarctica. As the world faces the challenges of climate change and environmental degradation, the role of Antarctica in global research becomes even more critical. The continent serves as a vital laboratory for understanding these changes and developing strategies for mitigation and adaptation.
The future of Antarctica depends on continued international cooperation and a commitment to protecting its unique environment. Sustainable practices, responsible tourism, and effective conservation measures are essential for preserving the continent for future generations. By working together, nations can ensure that Antarctica remains a place of peace, scientific discovery, and inspiration.
So, the next time you see a picture of a penguin or an iceberg, remember that Antarctica is more than just ice and snow. It’s a continent of international cooperation, scientific endeavor, and breathtaking beauty. It’s a place where nations come together to explore, understand, and protect a vital part of our planet. Isn’t that something truly special?
If you are looking for Antarctica Continent | The 7 Continents of the World you’ve came to the right web. We have 5 Pictures about Antarctica Continent | The 7 Continents of the World like Antarctica Map With Countries, Capitals, Cities, Roads And, 40% OFF, Antarctica Continent | The 7 Continents of the World and also List of Countries in Antarctica – Isolated Traveller. Read more:
Antarctica Continent | The 7 Continents Of The World
www.whatarethe7continents.com
antarctica continent continents world facts map maps
List Of Countries In Antarctica | Isolated Traveller

isolatedtraveller.com
Antarctica Map Countries Shop Stores | Pinnaxis.com

pinnaxis.com
Antarctica Map With Countries, Capitals, Cities, Roads And, 40% OFF
elevate.in
List Of Countries In Antarctica – Isolated Traveller

isolatedtraveller.com
Antarctica continent continents world facts map maps. List of countries in antarctica. Antarctica continent